Nephrology is the internal medicine subspecialty concerned with the diagnosis and management of people with kidney problems. Because the organ has so many vital jobs, nephrologists are experts in diagnosing and treating basic kidney issues and the systemic effects of renal impairment. Nephrologists’ careers are most often summoned to assist in management of more complex or advanced nephrology processes, and while the care of early kidney disease is a large part of related to internal medicine practice.
Doctors treat conditions such as primary kidney disorders (particularly diseases of the glomeruli (including uremic syndrome or diabetic nephropathy), tubular dysfunctions, and chemical effects on the kidney, including many drugs and diagnostic agents. Fellowship in practice of nephrology shall entail knowledge of nephrology disorders, collecting system and bladder including nephrolithiasis and issue of vasculature, infections and kidney tumors. The main job of nephrologists is to know intimately how kidneys are involved in other medical disorders (for example serve as valuable or heart failure), and because kidneys essential for keep blood pressure, they know how to manage hypertension too, especially when difficult to control. Another area where nephrologists’ diploma can help is the management of fluid osmotic and acid-base derangements especially when the kidney disease is advanced. Nephrology is vital for every patient who needs renal replacement therapy through treatment (hem dialysis and dialysis) supervision and participates in the organ transplant method when required. Most physicians practice alone or in small groups, providing consultations to other doctors and caring for chronic kidney disease patients over time. Nephrologists may also provide in-hospital consultation as part of their profession. Furthermore, nephrologists oversee the operation of dialysis centers, which can be integrated into their own practice, separate from their practice or a department of a hospital. Some run offices that are a mix of nephrology and PA patients. Nephrologists practice in the academic environment in which they provide hospital- and office-based care to patients through both continuous and outpatient consultative care, conduct basic and clinical research on the various maladies affecting the kidneys, and teach physician-students and residents.
Nephrology is the branch of medicine concerned with the study and treatment of kidney diseases, including electrolyte imbalances and hypertension, and the care of those requiring renal replacement therapy, such as dialysis and kidney transplants. The word "dialysis" has its origin in the middle of the 19th century and stems from the Greek word "dialysis," itself derived from the combining forms of "dialuein" (split, separate), "dia" (apart), and "luein" (set free). In other words, dialysis replaces the kidney’s most important (excretory) job of separating (and removing) excess water and toxins from the blood and eliminating them in urine. Many kidney diseases are systemic diseases that affect more than just the organ and require specialized care. These can be congenital or inherited conditions, such as polycystic kidney disease, or acquired diseases such as systemic vasculitis and autoimmune diseases. Patients are referred to nephrologists because of various conditions after a urinalysis is performed, including acute kidney injury, kidney disease, proteinuria, kidney stones, hypertensive, and balancing problems of acid-base or electrolyte.
There are few nephrology classes each having very vast facets of medication. Nephrology courses are available in different levels in order to better prepare potential healthcare professionals for their careers. There are a range of nephrology courses for applicants to choose from and enroll in the one that best fits their needs and future goals. Here are some of the most notable nephrology courses.
Graduate Programs:
MBBS (Master of Dental surgery): This four and a half-year curriculum requires a minimum grade of XII or equivalent in physics, chemistry, and biology to be passed to be eligible.
Master's Programs:
MD(General Medicine): After doing your MBBS, you can go for MD (General Medicine) programmed. The course is a three-year course. It is a continuing medical education degree focusing on the kidneys and kidney-related disorders.
Doctoral programmers
You may then apply for a DNB in Nephrology or Doctor of Medicine (DM) in Nephrology after receiving your graduate degree. The duration of this programmed is three years. You would be able to work as nephrologists training after obtaining the MCI registration.
Specialties and Syllabus of Courses in Nephrology
The professional should be able to implant standards after attaining the subjects at the following levels. Let us analyze the topics which were offered at the different levels.
Nephrology careers
And these students support their own bachelor's, master's, and doctoral degrees in nephrology to pursue careers as nephrologists, pediatric nephrologists, transplant nephrologists, urologists, interventional nephrologists, and other specialties to showcase their remarkably powerful gifts. There are many job opportunities for freshmen and people searching for jobs in the public and commercial sectors. Here is a list of some high-income career paths:
Nephrologists: A nephrologist specializes in the treatment of kidney diseases. They are also very acutely aware of how kidney disease or kidney malfunction can affect other places in your body. Nephrologists specialize in disorders that particularly target the kidneys.
A pediatric nephrologist has the necessary expertise to care for your child, whether he or she has kidney or urinary tract disorders, kidney stones, bladder problems or high blood pressure. This takes care of children from early childhood until late adolescence and, at some facilities, young adulthood.
 Diabetology Course
Diabetology Course Family Medicine
Family Medicine Cardiology
Cardiology Pediatrics
Pediatrics Rheumatology Courses
Rheumatology Courses Emergency Medicine Course
Emergency Medicine Course Endocrinology Course
Endocrinology Course MBA in Hospital Management
MBA in Hospital Management Hospital Management Courses
Hospital Management Courses PhD in Healthcare
PhD in Healthcare Master Class in Gynecology & Obstetrics
Master Class in Gynecology & Obstetrics Ultrasound Training Courses
Ultrasound Training Courses 2D Echo
2D Echo Fellowship in Diabetology
Fellowship in Diabetology Fellowship in Cosmetology
Fellowship in Cosmetology Fellowship In Critical Care Medicine
Fellowship In Critical Care Medicine Fellowship in Epidemiology and Biostatistics
Fellowship in Epidemiology and Biostatistics Fellowship in Infectious Diseases
Fellowship in Infectious Diseases Fellowship in Intensive Care Medicine
Fellowship in Intensive Care Medicine Fellowship in Internal Medicine
Fellowship in Internal Medicine Hair Transplant Training Courses
Hair Transplant Training Courses Infertility Training Courses
Infertility Training Courses IVF Training Courses
IVF Training Courses Aesthetic Medicine Courses
Aesthetic Medicine Courses Gastroenterology
Gastroenterology Pulmonology Courses
Pulmonology Courses Oncology Courses
Oncology Courses Fellowship in Echocardiography
Fellowship in Echocardiography Certificate Course in Diabetes
Certificate Course in Diabetes Fellowship in Obstetrics and Gynaecology
Fellowship in Obstetrics and Gynaecology Fellowship in Cardiology
Fellowship in Cardiology Fellowship in Gastroenterology
Fellowship in Gastroenterology Fellowship in Emergency Medicine
Fellowship in Emergency Medicine Fellowship in Pulmonology
Fellowship in Pulmonology Fellowship in Pediatrics
Fellowship in Pediatrics Fellowship in Oncology
Fellowship in Oncology Fellowship in Endodontics
Fellowship in Endodontics Fellowship in Nutrition
Fellowship in Nutrition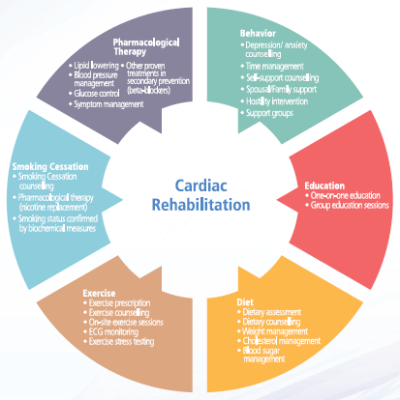 Fellowship in Cardiac Rehabilitation
Fellowship in Cardiac Rehabilitation Fellowship in Neurological Rehabilitation
Fellowship in Neurological Rehabilitation Fellowship in Orthopedics Rehabilitation
Fellowship in Orthopedics Rehabilitation Fellowship in Sports Rehabilitation
Fellowship in Sports Rehabilitation Fellowship in Family Medicine
Fellowship in Family Medicine Diabetes Courses for Doctors
Diabetes Courses for Doctors PG Diploma in Infectious Diseases
PG Diploma in Infectious Diseases Fellowship in Embryology
Fellowship in Embryology Fellowship in Gynecology and Obstetrics
Fellowship in Gynecology and Obstetrics Fellowship in Clinical Oncology
Fellowship in Clinical Oncology Fellowship in Preventive Cardiology
Fellowship in Preventive Cardiology Fellowship in Clinical Nutrition
Fellowship in Clinical Nutrition Fellowship in Nephrology
Fellowship in Nephrology Fellowship in Musculoskeletal Ultrasound
Fellowship in Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Fellowship in Emergency Ultrasound
Fellowship in Emergency Ultrasound Fellowship in Clinical Cardiology
Fellowship in Clinical Cardiology Fellowship in Non Invasive Cardiology
Fellowship in Non Invasive Cardiology Fellowship after MBBS
Fellowship after MBBS Online Courses After MBBS
Online Courses After MBBS Diploma After MBBS
Diploma After MBBS Post MBBS Diploma Courses
Post MBBS Diploma Courses